Background:
- Historical Ties: Ukraine and Russia share historical, cultural, and linguistic ties, and were part of the same Soviet empire for decades.
- Independence: Ukraine declared independence from the USSR in 1991, leading to tensions with Russia over its sovereignty.
- Crimea Annexation: In 2014, Russia annexed Crimea, a Ukrainian peninsula with a majority Russian population, sparking international condemnation.
- Donbas Conflict: Pro-Russian separatists in the Donbas region of eastern Ukraine declared independence in 2014, leading to a protracted conflict.
The War:
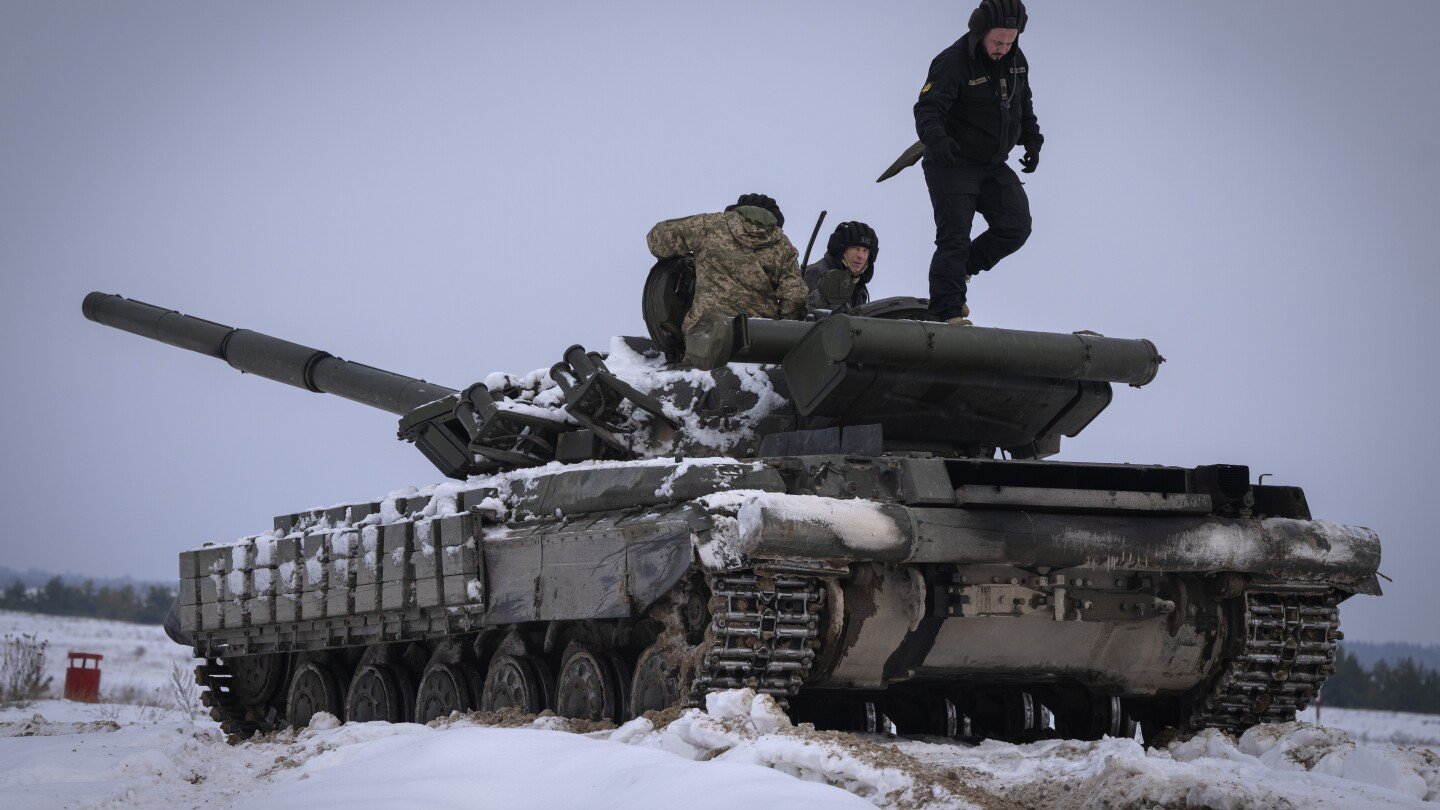
- Invasion: On February 24, 2022, Russia launched a full-scale invasion of Ukraine, citing the need to “denazify” and “demilitarize” the country.
- Objectives: Russia’s stated goals include:
- Control over all of Ukraine’s eastern regions (Donbas).
- Securing a land corridor to Crimea.
- Preventing Ukraine from joining NATO.
- Key Battles: The war has seen fierce battles in major cities like Kyiv, Mariupol, Kharkiv, and Kherson.
- Military Situation:
- Russia has sustained heavy losses in personnel and equipment.
- Ukrainian forces have mounted a strong resistance, aided by Western weapons and intelligence.
- The war has become a protracted conflict with both sides experiencing significant casualties.
Russia-Ukraine war impacts
The Russia-Ukraine war has had far-reaching and profound impacts on the world, affecting economies, energy markets, food security, geopolitical relations, and even the global security architecture. Here’s a breakdown of some key impacts:
Economic Impacts:
- Inflation and Cost of Living: The war has driven up global energy prices (oil and gas) due to sanctions on Russia and supply chain disruptions, contributing significantly to inflation worldwide. This has increased the cost of living for people globally.
- Recession Fears: The war has exacerbated existing economic challenges, leading to fears of a global recession. Supply chain disruptions, energy shortages, and uncertainties in the global markets are creating economic instability.
- Financial Market Volatility: The war has caused significant volatility in financial markets, with stock markets experiencing swings and investors seeking safe havens.
Energy Impacts:
- Energy Crisis: The war has created an energy crisis in Europe, which was heavily reliant on Russian gas. Sanctions and reduced gas flows have led to energy rationing, higher prices, and concerns about energy security.
- Shifting Energy Landscape: The war is accelerating the transition to renewable energy sources and diversifying energy supplies away from Russia.
Food Security Impacts:
- Global Food Shortages: Russia and Ukraine are major exporters of wheat, barley, and other agricultural products. The war has disrupted these exports, leading to food shortages and price hikes, particularly in developing countries.
- Hunger Crisis: The war has exacerbated existing hunger crises, particularly in Africa and the Middle East, where many countries rely on Ukrainian grain imports.
Geopolitical Impacts:
- Strengthened NATO: The war has led to a surge in NATO membership applications from Finland and Sweden, strengthening the alliance and demonstrating its continued relevance.
- Increased Tensions: The war has heightened geopolitical tensions between Russia and the West, leading to a new Cold War-like standoff.
- Emerging Alliances: The war is reshaping global alliances, with some countries choosing sides and others seeking neutrality.
Security Impacts:
- Nuclear Threat: Russia’s nuclear threats have raised concerns about a potential escalation of the conflict and the possibility of a nuclear war.
- Weakening of International Order: The war has undermined the international order based on rules and diplomacy.
- Arms Race: The war has spurred an arms race, with countries increasing military spending and modernizing their arsenals.
Other Impacts:
- Humanitarian Crisis: Millions of Ukrainians have been displaced, and thousands have been killed. The war has created a humanitarian crisis requiring international aid.
- Environmental Impacts: The war has led to significant environmental damage, including pollution and destruction of ecosystems.
Long-Term Implications:
- Global Order Reshaping: The war is likely to have lasting effects on the global order, including the balance of power, alliances, and international institutions.
- Economic Restructuring: The war could accelerate the shift towards a multipolar world with new economic centers emerging.
- Technological Advancements: The war is likely to drive technological advancements in areas like cyberwarfare, artificial intelligence, and drone technology.
Key issues:
The Russia-Ukraine war is a complex conflict with a multitude of interconnected issues at its core. Here are some of the key issues driving the conflict:
- Historical and Cultural Ties:
- Shared History: Ukraine and Russia have a long and complex shared history, having been part of the same empire for centuries. This shared history leads to overlapping cultural and linguistic ties, making the conflict deeply emotional and personal.
- Russian Influence: Russia has historically exerted significant influence over Ukraine, often viewing it as part of its sphere of influence. This has led to tensions over Ukraine’s sovereignty and independence.
- NATO Expansion:
- Russian Security Concerns: Russia has long expressed concerns about NATO expansion eastward, viewing it as a threat to its security. The potential inclusion of Ukraine in NATO, which shares a border with Russia, was a major point of contention for Moscow.
- Western Security Guarantees: Ukraine’s aspiration to join NATO reflects a desire for Western security guarantees, seen by Russia as a direct challenge to its interests.
- Territorial Disputes:
- Crimea Annexation: In 2014, Russia annexed the Crimean Peninsula, a territory with a majority Russian population, claiming it was a historical part of Russia. This annexation was condemned by the international community.
- Donbas Conflict: The Donbas region in eastern Ukraine has been the scene of a protracted conflict since 2014, with pro-Russian separatists backed by Moscow fighting for independence. Russia has consistently supported these separatists, adding to tensions with Ukraine and the West.
- Identity and Self-Determination:
- Ukrainian Identity: Ukraine, after gaining independence from the Soviet Union in 1991, has been striving to establish its own national identity, distinct from Russia. This has been a source of friction with Moscow, which seeks to maintain its cultural and political influence.
- Russian Narrative: Russia has promoted a narrative of “denazifying” and “demilitarizing” Ukraine, arguing that it needs to protect Russian speakers and prevent Ukraine from joining NATO. This narrative, however, is widely contested by the international community.
- Geopolitical Power Struggle:
- Global Order: The conflict is part of a broader geopolitical struggle for power and influence between Russia and the West. Russia is seeking to assert its position as a major power and challenge the existing global order.
- Western Interests: The West, through its support for Ukraine, is seeking to protect its interests in Europe and the broader international order, opposing Russia’s assertive actions.
- Economic Interests:
- Resource Control: Ukraine is rich in natural resources, including fertile agricultural land, and Russia has sought to exert control over these resources.
- Economic Influence: Russia’s economic influence on Ukraine has been a source of leverage for Moscow, and the war has disrupted this economic relationship.
- Human Rights:
- Allegations of War Crimes: There have been numerous reports of war crimes committed by both sides in the conflict, raising concerns about the humanitarian cost of the war.
- Civilian Casualties: The war has caused a massive displacement of civilians and led to a significant number of civilian casualties, highlighting the human cost of the conflict.
- Nuclear Threats:
- Escalation Risks: Russia’s nuclear threats have heightened concerns about the possibility of a wider escalation of the conflict, potentially leading to a nuclear war.
- Global Consequences:
- Economic Impacts: The war has had a significant impact on global economies, leading to inflation, supply chain disruptions, and fears of a global recession.
- Energy Crisis: The war has exacerbated the global energy crisis, leading to higher energy prices and concerns about energy security.
- Food Security: The conflict has disrupted global food supply chains, particularly for wheat and other grains, raising concerns about global food shortages.
Conclusion:
The Russia-Ukraine war is a complex and ongoing conflict with significant implications for the international security order and global stability. The war’s resolution remains uncertain, and the consequences for all involved are likely to be profound and long-lasting.