
CPEC: A Detailed Note with Explanation
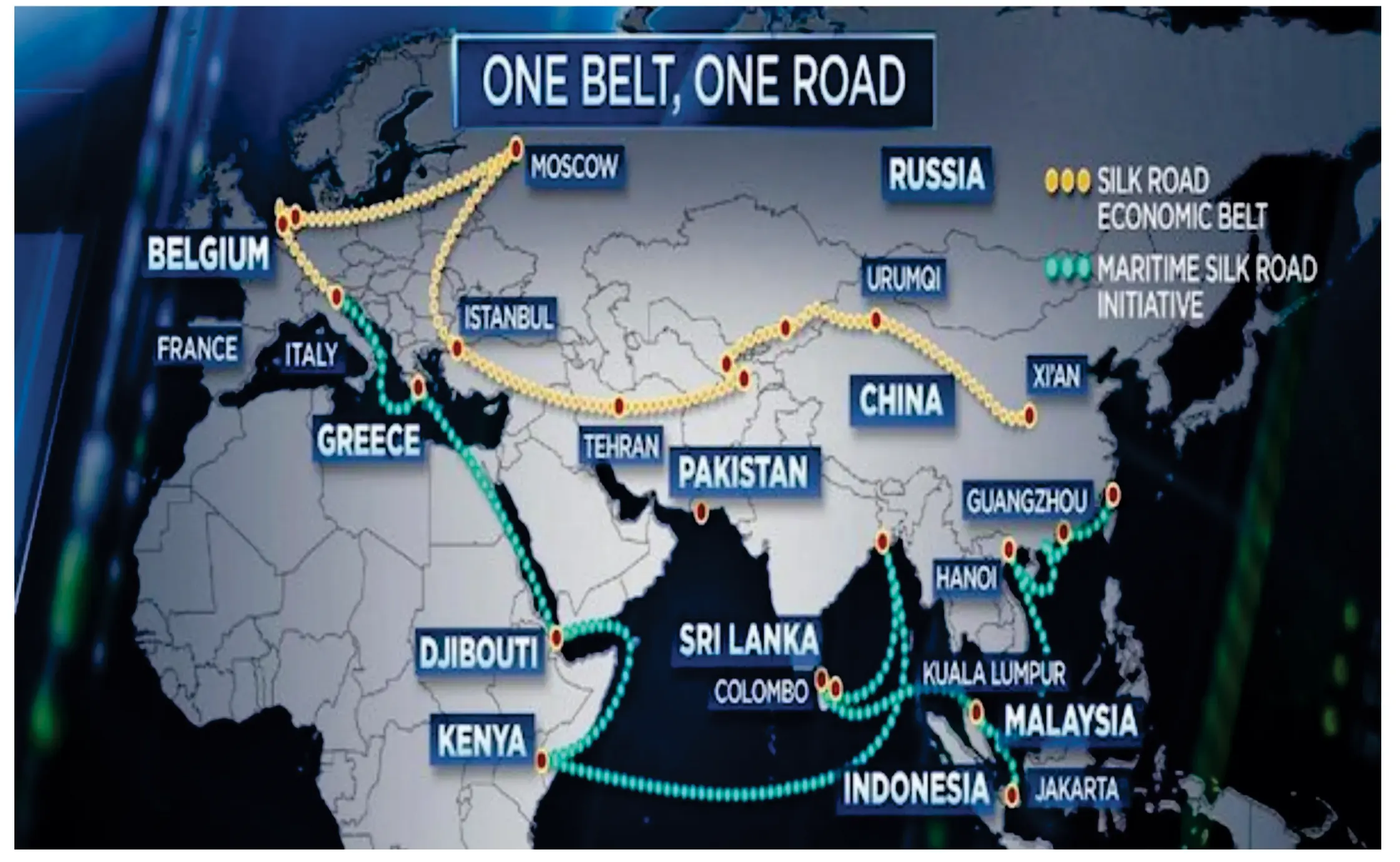
CPEC, short for China-Pakistan Economic Corridor, is a collection of infrastructure projects under the umbrella of China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI). Launched in 2013, CPEC is a flagship project of BRI, aiming to connect China’s Xinjiang province to Pakistan’s Gwadar Port on the Arabian Sea.
Key Features of CPEC:
Connectivity: Building a network of roads, railways, and pipelines to enhance trade and transportation between China and Pakistan, as well as providing China with a shorter and more secure trade route to the Middle East and Africa.
Energy Cooperation: Addressing Pakistan’s chronic energy shortages by developing power plants, mainly coal, hydropower, and renewable energy sources.
Economic Zones and Industrial Development: Establishing special economic zones and industrial parks to attract investment, create jobs, and boost economic growth in Pakistan.
Social Development: Investing in social development projects, including education, healthcare, and poverty alleviation programs, to improve the living standards of Pakistani citizens.
Explanation and Analysis:
CPEC is a cornerstone of China-Pakistan relations and holds significant strategic importance for both countries.
For Pakistan:
Economic Boost: CPEC is envisioned as a game-changer for Pakistan’s economy, addressing its infrastructure deficit, attracting foreign investment, and creating employment opportunities.
Energy Security: CPEC projects can alleviate Pakistan’s energy shortages, supporting economic growth and industrial development.
Geopolitical Significance: CPEC strengthens Pakistan’s relationship with China, a key ally and economic partner, providing a counterbalance to its relationship with the United States.
For China:
Access to the Arabian Sea: CPEC provides China with a shorter and more direct trade route to the Middle East, Africa, and Europe, bypassing the longer and potentially less secure Strait of Malacca.
Strategic Foothold in South Asia: CPEC enhances China’s strategic influence in South Asia, a region of vital geopolitical importance.
Economic Opportunities: CPEC opens up new markets for Chinese goods and services, providing opportunities for Chinese companies to invest and operate in Pakistan.
Criticisms and Concerns:
Despite its potential benefits, CPEC has faced criticism and concerns:
Debt Trap Diplomacy: Critics argue that Pakistan’s mounting debt to China could jeopardize its economic sovereignty, making it vulnerable to Chinese influence.
Lack of Transparency: Concerns exist regarding the transparency of CPEC projects, including bidding processes and project implementation, raising questions about potential corruption and environmental damage.
Security Concerns: CPEC infrastructure projects traverse through sensitive regions, including Balochistan, a province facing separatist insurgency, posing security risks.
Impact on Local Communities: Concerns exist about the potential displacement of local communities and the environmental impact of large-scale infrastructure projects.
Conclusion:
CPEC is a complex and ambitious project with the potential to significantly impact the economies and geopolitics of both China and Pakistan. While it offers potential economic benefits and strengthens bilateral ties, it also raises concerns regarding debt sustainability, transparency, and security. The ultimate success of CPEC will depend on how both countries address these challenges and ensure the project benefits all stakeholders involved.



I want to to thank you for this great read!!
I definitely loved every bit of it. I’ve got you bookmarked to look at new
things you post…
You can certainly see your enthusiasm within the article you
write. The sector hopes for more passionate writers
such as you who are not afraid to mention how they believe.
All the time go after your heart.
Your method of explaining all in this paragraph is genuinely
pleasant, all be capable of without difficulty be aware of it, Thanks a
lot.
I’m not sure exactly why but this blog is loading very slow for me.
Is anyone else having this issue or is it a issue on my end?
I’ll check back later and see if the problem still exists.
Just want to say your article is as astounding.
The clearness in your post is just spectacular and
i can assume you are an expert on this subject. Well with your permission let
me to grab your feed to keep up to date with forthcoming post.
Thanks a million and please carry on the gratifying work.
Hello everyone, it’s my first pay a quick visit at this website, and article is genuinely
fruitful in favor of me, keep up posting such posts.
Hello, its nice paragraph on the topic of media print, we all know media is a
impressive source of facts.
Good day! I could have sworn I’ve visited this site before but after browsing through some of
the articles I realized it’s new to me. Anyways, I’m
certainly pleased I discovered it and I’ll be book-marking it and checking back frequently!
Hey there! I’ve been following your weblog for a while now and finally got the courage to go ahead and
give you a shout out from Kingwood Texas! Just wanted to mention keep up the good job!
Fabulous, what a weblog it is! This weblog gives valuable data to us, keep it up.
As the admin of this web site is working, no uncertainty very soon it will be famous, due to its quality contents.
I am not sure where you’re getting your info, but good topic.
I needs to spend some time learning much more or understanding more.
Thanks for magnificent information I was looking for this info for my mission.
Hello! I know this is somewhat off topic but I was
wondering if you knew where I could locate a captcha plugin for my comment form?
I’m using the same blog platform as yours and
I’m having trouble finding one? Thanks a lot!
Hello, i feel that i noticed you visited my blog so i came to return the favor?.I am attempting to in finding things to enhance my site!I guess
its good enough to use a few of your ideas!!
Hello there, You’ve done a great job. I will definitely digg
it and personally recommend to my friends. I am sure they’ll be benefited from this website.